#Fluorescent Microscope
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Microscope Manufacturers & Suppliers in India

Many microscope manufacturers and suppliers worldwide offer different kinds of quality optical, digital, and electron microscopes for educational, medical, and industrial purposes. Due to the state of the art technology and advanced precision manufacturing capabilities the manufacturers put great emphasis on quality imaging and durability. They are trusted all over the world and are committed to customer service, product quality, price, and customized solutions for all laboratory and research purposes. Experienced top quality microscope solutions with Infinity Optics - leading manufacturers and suppliers of microscopes in India. The motors driving Infinity Optics is precision, reliability, and innovation, so please go ahead and experience the advanced optical instruments offered by Infinity Optics.
#Inverted microscope#Fluorescent Microscope#Microscope Manufacturers in India#Microscope Suppliers#Laboratory Microscope Suppliers#Microscope Manufacturer in Ambala#Laboratory Equipment Manufacturers in India#Lab Equipment Suppliers in India#Stereo Zoom Microscope Supplier#Multi View Microscope#Upright Fluorescent Microscope#Research Microscope#Microscope Manufacturers & Suppliers in India
2 notes
·
View notes
Text









i've been mixing flesh, wax, chemicals and dyes for months to obtain these images
#first one look like a skull??#flesh wizard#i modified them for esthetical purpose only here ahah#but maybe its gonna be my first paper omgg#ik its an artblog but can we agree that this count??#fluorescence#science#cells#biology#immunofluorescence#microscopy#medecine#medblr#pathology#skull#retrowave#synthpop#synthwave#neon light#microscope
274 notes
·
View notes
Text
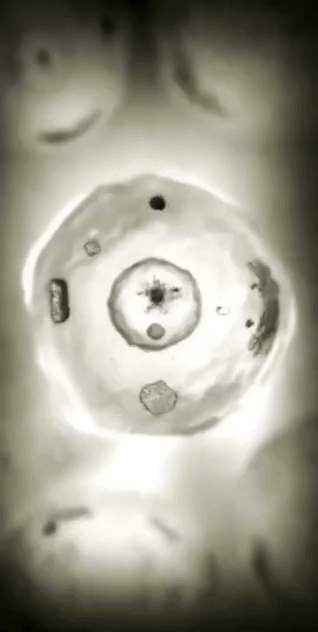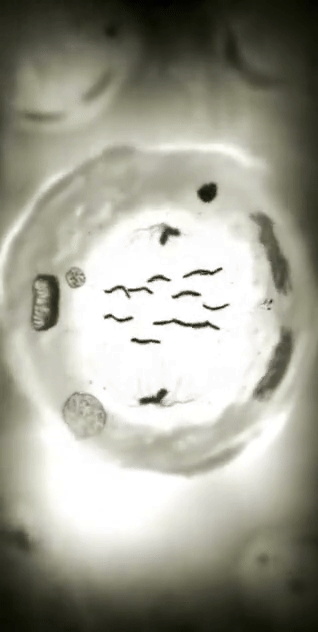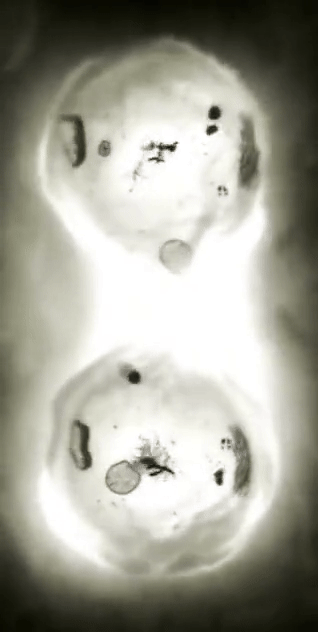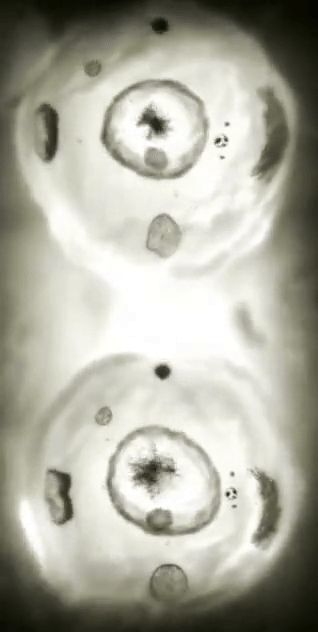
Every second, millions of cells in our bodies undergo mitosis, a fundamental process that ensures growth, repair, and development. From a single parent cell, identical daughter cells emerge, each carrying the same genetic information. This intricate dance of chromosomes and cellular structures keeps life going!
#cells#biology#photography#explore#nature#science#adorable#education#lol#amazing#awesome#funny#microscope#fluorescence#tissue#growth#cell division#nucleus#nuclei#centrioles#prophase#metaphase#anaphase#telophase#cytokinesis#mitosis#chromosomes#dna#microtubules#spindle
35 notes
·
View notes
Text

Fluorescence microscope image
12 notes
·
View notes
Text
im literally soooo cute
#and so is my girlfriend. but we're talking about me rn#also i am smart! and funny! and people like me#and i have several friends#and i am a good cook. and i can knit. and operate basically any fluorescence microscope incl TIRF and STED and so on#and i give excellent feedback on presentations and experimental ideas#and my girlfriend is so in love with me because of all of these things.#ok we can talk about them also a bit i guess#box opener#😊.
10 notes
·
View notes
Text

A Journey into the World of Microscopy: From Humble Beginnings to High-Tech Magnification
The science of looking into the hidden invisible Microscopy has transformed our understanding of the world around us. It can explore the universe beyond the reach of our naked eyes, with complex cellular structures, red blood cells, viruses and other viruses and microorganisms taking on amazing perspectives
The history of the microscope is a fascinating story of human curiosity, scientific genius, and relentless exploration. From the humble beginnings of simple magnifying glasses to the sophistication of modern electronic microscopes, the invention of microscopes has shaped our understanding of the microscopic world
In the 1600s, Dutch opticians such as Hans and Zachary Janssen are credited with inventing the first microscope. Known for this hybrid microscope, many lenses were used to magnify objects up to 30 times.At the end of the 17th century, Antony van Leeuwenhoek, Dutch draper some changed our perception of thumbnails. Armed with a well-made single-lens microscope, and explored the hidden reaches of nature. In 1674, Leeuwenhoek discovered microorganisms in lake water, which he aptly named “animalcules”. His discovery laid the foundations of biology and inspired generations of scientists. This incredible feat allowed him to uncover a hidden universe – the first sightings of bacteria, red blood cells, and other microorganisms.
Formation of the scientific environment (17th-19th centuries): Leeuwenhoek’s discoveries boosted scientific research. Robert Hooke, an English scientist, established these developments. In 1665, his book "Micrographia" recorded his observations with a compound microscope. Notably, the term "cell" was coined by Hooke when he examined cork tissue, laying the foundation for cell biology.Microscope systems flourished throughout the 18th and 19th centuries Joseph Lister and other scientists addressed the limitations of the early lenses, introducing improvements that reduced image distortion.
Beyond the Limits of Light: The Beginning of the New Age (19th-20th century): As the 19th century progressed, the limitations of optical microscopy became apparent and scientists yearned for a tool which can go deeper into cells. This research culminated in the development of the electron microscope in the 1930s. The 20th century was revolutionary with the invention of the electron microscope. Unlike light microscopes, which use visible light, electron microscopes use electron beams to achieve much higher magnification.Formation of the scientific environment (17th-19th centuries): Leeuwenhoek’s discoveries boosted scientific research. Robert Hooke, an English scientist, established these developments. In 1665, his book "Micrographia" recorded his observations with a compound microscope. Notably, the term "cell" was coined by Hooke when he examined cork tissue, laying the foundation for cell biology.Microscope systems flourished throughout the 18th and 19th centuries Joseph Lister and other scientists addressed the limitations of the early lenses, introducing improvements that reduced image distortion.
Beyond the Limits of Light: The Beginning of the New Age (19th-20th century): As the 19th century progressed, the limitations of optical microscopy became apparent and scientists yearned for a tool which can go deeper into cells. This research culminated in the development of the electron microscope in the 1930s. The 20th century was revolutionary with the invention of the electron microscope. Unlike light microscopes, which use visible light, electron microscopes use electron beams to achieve much higher magnification.
In the 1930s, German experts Max Knoll and Ernst Ruska made the first electron microscope. This tool let us see tiny things like cells and even atoms by using electron beams, not light, getting images many times bigger. This cool invention showed us the tiny parts inside cells, viruses, and stuff too small to see before. The 1900s brought even more cool microscopes. New kinds like phase-contrast and confocal microscopy let scientists look at live cells without using stuff that could hurt them. Now, the world of looking at tiny things is getting even better. Today, we have high-tech microscopes that use computers and lasers. These let us see and even change tiny things in ways we never could before.
Modern Microscopy's Diverse Arsenal - Today, the field of microscopy boasts a diverse range of specialized instruments, each tailored to address specific scientific needs. Here's a glimpse into some remarkable examples:
Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM): Imagine a high-tech camera that captures images using a beam of electrons instead of light. That's the essence of a SEM. By scanning the surface of a sample with a focused electron beam, SEMs generate detailed information about its topography and composition. This makes them ideal for studying the intricate structures of materials like insect wings, microchips, and even pollen grains.
Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM): While SEMs provide exceptional surface detail, TEMs take us a step further. They function by transmitting a beam of electrons through a very thin sample, allowing us to observe its internal structure. TEMs are the go-to instruments for visualizing the intricate world of viruses, organelles within cells, and macromolecules like proteins.
Confocal Microscopy: Ever wished to focus on a specific layer within a thick biological sample and blur out the rest? Confocal microscopy makes this possible. It utilizes a laser beam to precisely illuminate a chosen plane within the sample, effectively eliminating information from out-of-focus regions. This allows researchers to create sharp, three-dimensional images of cells, tissues, and even small organisms.
Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM): This technique takes a completely different approach, venturing into the realm of physical interaction. AFM employs a tiny cantilever, akin to a microscopic feeler, to physically scan the surface of a sample. By measuring the minute forces between the cantilever and the sample's surface, AFM can map its topography at an atomic level. This provides invaluable insights into the properties of materials at an unimaginable scale, making it crucial for research in fields like nanotechnology and surface science.
Fluorescence Microscopy: Imagine illuminating a sample with specific wavelengths of light and observing it glowing in response. That's the essence of fluorescence microscopy. This technique utilizes fluorescent molecules or tags that bind to specific structures within a cell or tissue. When excited by light, these tags emit their own light, highlighting the target structures with remarkable clarity. This allows researchers to visualize specific proteins, DNA, or even pathogens within biological samples.
Super-resolution Microscopy (SRM): Overcoming the limitations imposed by the wavelength of light, SRM techniques like STED (Stimulated Emission Depletion) and PALM (Photoactivated Localization Microscopy) achieve resolutions surpassing the diffraction limit. This allows researchers to visualize structures as small as 20 nanometers, enabling the observation of intricate cellular machinery and the dynamics of individual molecules within living cells.
Cryo-Electron Microscopy (Cryo-EM): This powerful technique takes a snapshot of biological samples in their near-life state. Samples are rapidly frozen at ultra-low temperatures, preserving their native structure and minimizing damage caused by traditional fixation methods. Cryo-EM has been instrumental in determining the three-dimensional structures of complex molecules like proteins and viruses, providing crucial insights into their function and potential drug targets.
Correlative Microscopy: Combining the strengths of multiple microscopy techniques, correlative microscopy offers a comprehensive view of biological samples. For instance, researchers can utilize fluorescence microscopy to identify specific structures within a cell and then switch to electron microscopy to examine those structures in high detail. This integrated approach provides a deeper understanding of cellular processes and their underlying mechanisms.
Light Sheet Microscopy (LSM): Imagine illuminating a thin slice of a sample within a living organism. LSM achieves this feat by focusing a laser beam into a thin sheet of light, minimizing photobleaching and phototoxicity – damaging effects caused by prolonged exposure to light. This allows researchers to observe dynamic processes within living organisms over extended periods, providing valuable insights into cellular behavior and development.
Expansion Microscopy (ExM): This innovative technique physically expands biological samples by several folds while preserving their structural integrity. This expansion allows for better resolution and visualization of intricate cellular structures that would otherwise be difficult to distinguish using traditional microscopy methods. ExM holds immense potential for studying the organization and function of organelles within cells.
Scanning Near-Field Optical Microscopy (SNOM): This innovative technique pushes the boundaries of resolution by utilizing a tiny probe that interacts with the sample at an extremely close range. SNOM can not only image the surface features of a sample with exceptional detail but also probe its optical properties at the nanoscale. This opens doors for research in areas like material science and photonics, allowing scientists to study the behavior of light at the interface between materials.
X-ray Microscopy: Stepping outside the realm of light and electrons, X-ray microscopy offers unique capabilities. By utilizing high-energy X-rays, this technique can penetrate deep into samples, making it ideal for studying the internal structure of dense materials like bones and minerals. Additionally, it allows for the visualization of elements within a sample, providing valuable information about their distribution and composition.
From revealing the building blocks of life to aiding in the development of new medicines, the microscope has played an undeniable role in shaping our scientific understanding. As technology continues to evolve, one can only imagine the future breakthroughs this remarkable invention holds in unveiling the secrets of our universe, both seen and unseen. These advancements hold the potential to revolutionize our understanding of biological processes, develop new materials with extraordinary properties, and ultimately pave the way for breakthroughs in medicine, nanotechnology, and countless other fields. As we continue to refine and develop novel microscopy techniques and the future holds immense promise for further groundbreaking discoveries that will undoubtedly revolutionize our perception of the world around us.
#science sculpt#life science#science#molecular biology#biology#biotechnology#artists on tumblr#microscopy#microscope#Scanning Electron Microscope#Transmission Electron Microscope#Confocal Microscopy#Atomic Force Microscopy#Fluorescence Microscopy#Expansion Microscopy#X-ray Microscopy#Super-resolution Microscopy#Light Sheet Microscopy#illustration#illustrator#illustrative art#education#educate yourself#techniques in biotechnology#scientific research#the glass scientists#scientific illustration#scientific advancements
7 notes
·
View notes
Text
youtube
The confocal microscope at Imperial College's Sir Alexander Fleming Building lab is used for imaging the interior of living plant and animal cells.
During my PhD project, I used the confocal microscope to view the interior of Nicotiana benthamiana plant cells which were expressing Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP) tagged genes of interest. I aimed to find out where the proteins encoded by the genes of interest were localised in the plant cell, which turned out to be in the cytoplasm.
From Wikipedia's entry on Confocal Microscopy: "Confocal microscopy, most frequently confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) or laser scanning confocal microscopy (LSCM), is an optical imaging technique for increasing optical resolution and contrast of a micrograph by means of using a spatial pinhole to block out-of-focus light in image formation. Capturing multiple two-dimensional images at different depths in a sample enables the reconstruction of three-dimensional structures (a process known as optical sectioning) within an object. This technique is used extensively in the scientific and industrial communities and typical applications are in life sciences, semiconductor inspection and materials science. Light travels through the sample under a conventional microscope as far into the specimen as it can penetrate, while a confocal microscope only focuses a smaller beam of light at one narrow depth level at a time. The CLSM achieves a controlled and highly limited depth of field."
Music by the Fiechter Brothers
Images by Katia Hougaard & the Facility for Imaging by Light Microscopy at Imperial College London
#katia plant scientist#botany#plant biology#plants#plant science#biology#science#science and technology#confocal microscopy#microscopy#microscope#scientific instruments#laboratory#research#phdblr#phd#phd life#molecular biology#cell biology#green fluorescent protein#plant scientist#Youtube
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
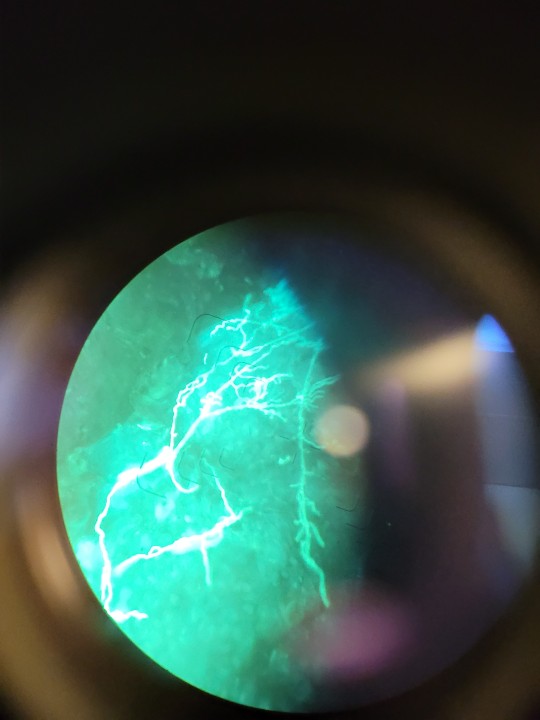

just wanted to share this very sweet calcoflour prep I did of a skin scraping that was absolutely heaving with a dermatophyte (mould) at work :) check those mycelia ouuuuut
2 notes
·
View notes
Text
I’ve counted pollen before-it really hurts your eyes when you do it through a light microscope

#the fluorescent microscope was so much easier#and the flower stigma photos I took were gorgeous#I might still have some I stole on my old laptop
42K notes
·
View notes
Text
#Fluorescence Microscopes#Fluorescence Microscope#Fluorescence Microscopes in india#Fluorescence Microscope in india#Fluorescence Microscope india#Fluorescence Microscopes india
0 notes
Text
How to Sell Digital Products without Social Media

You may want to sell digital products. And have been told to create an Instagram account or Tik Tok page to get traffic.
I am here to tell you that you do not need to have social media to sell digital products.
You can get free traffic and won't need any followers.
Digital products are a great way to earn passive income from home.
They are low cost to start. You won't have to worry about sending something in the mail.
As soon as your customers pay they get instant access to the product.
You can sell one digital product over and over again. You will not have to worry about stocking inventory or needing to purchase inventory.
The thing that I love about digital products is how much money and time I save.
I'm able to create using inexpensive tools that allow me to not only have a digital product but have a website to host the product and traffic to market the digital product.
Instagram, TikTok, Twitter and social media are not the only way to get traffic for your product.
Sometimes those platforms do more harm than good for your digital product business.
You are limited with how much content you can create on a social media platform. You are also limited to how frequently you can engage on the platform.
And the one thing about social media that I really don't like is how easily it can be taken from you without any real cause
Because they have such strong AI algorithms anything can cause your account to be taken from you. And it can be a minor misunderstanding.
Fighting to get your account back is so much stress. I have had so many Instagram accounts removed and suspended without cause. And when I tried to get them back I ran into another problem and another problem and even another problem.
I found a way to sell my digital products without needing social media. I found a way to sell my digital products without needing any followers. I found a way to market my digital products for free and it's not causing me any stress to create content for it.
If you want to be successful with growing your digital product business you're going to need traffic. You're going to need an audience for your digital product business.
Building a target audience is very important to the success and growth of your business.You want people who are willing to buy and people who are ready to buy.
This post right here teaches how to build your target audience using six important questions.
The Secret to Finding Your Ideal Audience (It Starts with These Questions!)
You don't only want a target audience for your digital product. But you need a niche that's going to sell. A niche that's going to help solve a problem. And be interesting enough for people to purchase it from you.
Having a good niche and a great target audience is a wonderful combination for the success of a digital product business.
Mix in some good traffic and you have a business that will bring you profits and results.
The reason why you don't need social media.
Social media may be popular but it's not necessary for the growth of your business and brand.
Many people think because it's social media and you can grow your following that means you will have a lot of sales. Because the more followers you have the more sales you'll receive.
But that is not true. Most followers don't see the content you post. And most followers are not buyers because people follow a page for many different reasons.
If you want your business to grow and thrive you need a system that gets your product in front of the right people.
A system that helps you save time and money. That doesn't frustrate you with content creation and growing a social media page.
And my course passive profit path teaches you how to build it.
I'm teaching you how to create your audience. I'm giving you 100 niches to choose from broken down into profitable categories. And how to get free traffic for your product.
You can have a digital product business without social media.
I'm getting free traffic everyday and I do not use Instagram, Twitter or TikTok.
I built my digital product business and I didn't pay $400 for a course.
I don't pay a monthly subscription for my website. And I can sell 1 product over and over again making as much money as I'd like.
I don't have to worry about inventory, monthly subscription fees, or keeping track of shipments.
And I did all this without any followers.
Everything I'm doing I'm teaching you in my course.
If you're ready to start your digital product business for less than $5 without using social media or building a following.
Take my course and learn how to build a profitable business and be ready to go within 30 days.

click here to take the course
Source: How to Sell Digital Products without Social Media
0 notes
Text
Premium Fluorescent Microscopes from Trusted Indian Manufacturers and Suppliers
Discover a wide range of high-performance fluorescent microscopes from leading Indian manufacturers and suppliers. These advanced microscopy solutions are ideal for various research, clinical, and industrial applications, offering exceptional imaging quality for fluorescence studies. With a focus on precision, durability, and innovation, these Indian suppliers provide top-tier instruments that cater to global demand. Rely on their expertise to deliver cutting-edge technology and reliable products for your fluorescence microscopy needs.
Indian Fluorescent Microscopes Manufacturer
Top Science Lab Equipment Manufacturers | FineLab UK
Indian Pharmacy Instruments & Global Manufacturers
Metallurgical Microscope Manufacturer | FineLab UK Corp
Stereo Zoom Microscope | FineLab UK Corporation
Understanding the Head of the Microscope
#head in microscope#head of microscope#head on microscope#head microscope#head of the microscope#Fluorescent Microscopes#Indian Fluorescent Microscopes#Fluorescent Microscopes Exporter#Fluorescent Microscopes Supplier#Indian Fluorescent Microscopes Manufacturer
0 notes
Text

Best Inverted Fluorescence Microscope Manufacturer in India
An inverted fluorescence microscope manufacturer specializes in the design and production of advanced optical instruments that allow for the observation of fluorescent specimens from below. These manufacturers focus on creating microscopes that utilize fluorescence techniques to illuminate samples, enabling researchers to study cellular structures and processes in detail. Coslab India, a leading manufacturer of inverted fluorescence microscopes, specializes in providing advanced imaging solutions for various scientific applications. Their innovative designs and cutting-edge technology cater to the needs of researchers and laboratories, ensuring high-quality performance and reliability in fluorescence microscopy. Mail: [email protected] Contact: +91-9416113230
#Inverted Fluorescence Microscope Manufacturer#Top Inverted Fluorescence Microscope Manufacturer#Best Inverted Fluorescence Microscope Manufacturer#Inverted Fluorescence Microscope Manufacturer in India
0 notes
Text
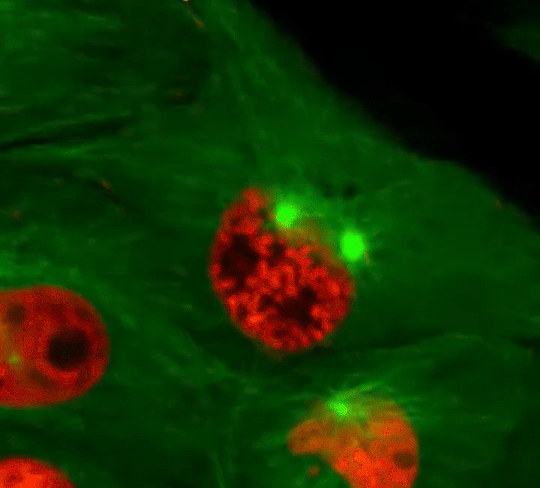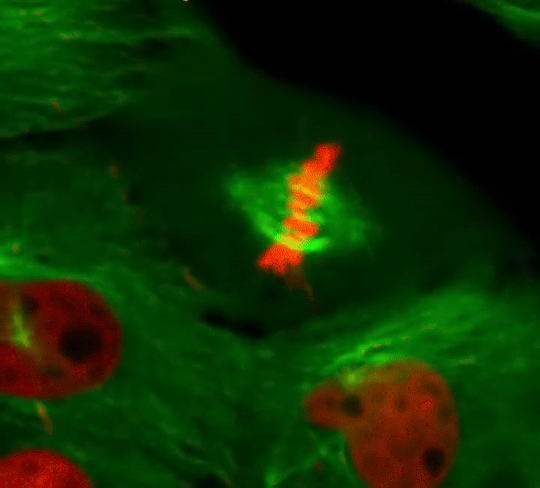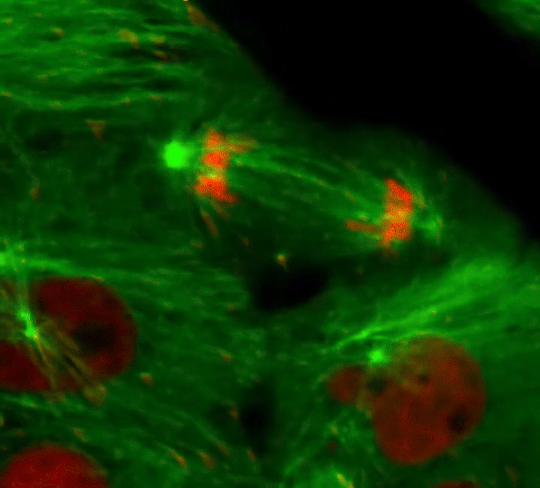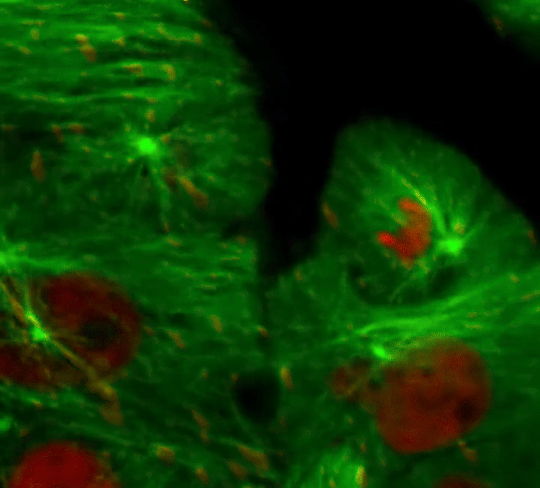
Cell Division: Stages of Mitosis
#cells#biology#photography#explore#nature#science#adorable#education#lol#amazing#awesome#funny#microscope#fluorescence#tissue#growth#cell division#nucleus#nuclei#centrioles#prophase#metaphase#anaphase#telophase#cytokinesis#mitosis#chromosomes#dna#microtubules#spindle
132 notes
·
View notes
Text

Convallaria under a fluorescence microscope.
10 notes
·
View notes
Text

#IFTTT#Flickr#eggplantskin#uvivf#365nm#zwb2#uvlight#fluorart#fluorescence#luminescence#ultraviolet#color#art#science#oldtor#mitutoyo#mplanapo#planapochromat#fujifilmxt5#microscope#micro#photomicrography#ultramacro#микрофото#флуоресценция#люминесценция#баклажанподмикроскопом#ультрафиолет#микроскопия#митутойо
0 notes
Text
1 note
·
View note